
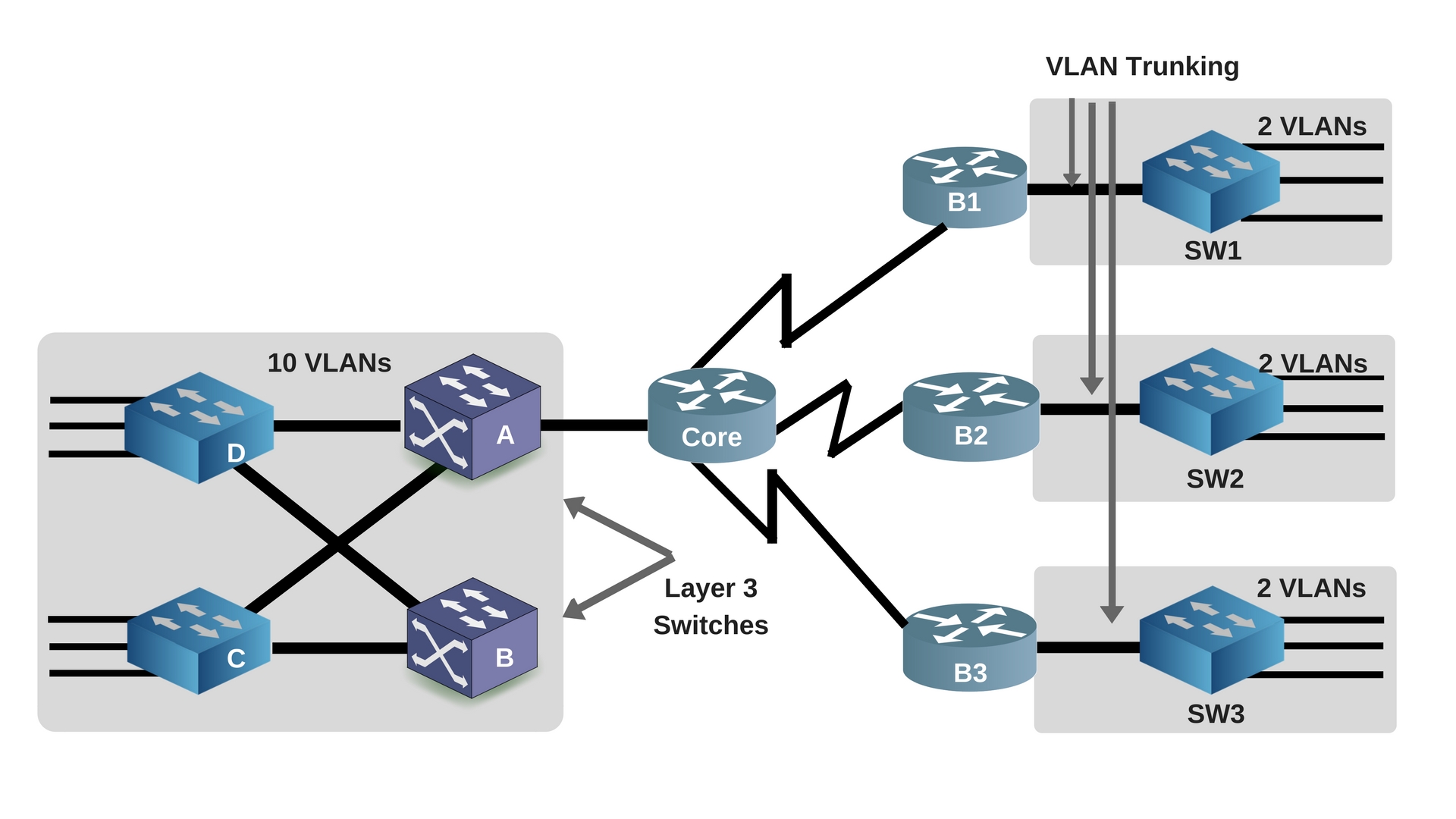
The figure below, shows how this process works. The user nodes in the VLANs forwards traffic to the router which then forwards the traffic to the destination network regardless of the VLAN configured on the switch. As we learnt previously, VLANs logically segment the switch into different subnets, when a router is connected to the switch, an administrator can configure the router to forward the traffic between the various VLANs configured on the switch. Inter-VLAN routing can be defined as a way to forward traffic between different VLAN by implementing a router in the network.
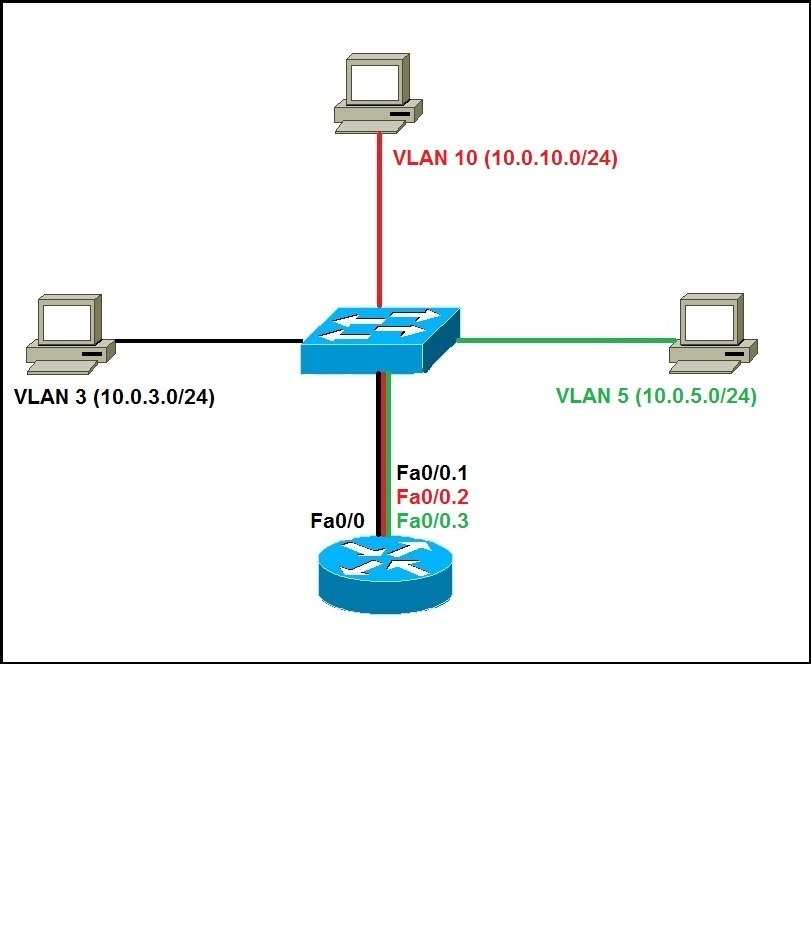
In this course, we will look at one type of inter-VLAN routing, which is through the use of a router. The way this can be accomplished is through inter-VLAN routing. In many cases, we may need connectivity between users located on different VLANs. Therefore, user nodes located on different VLANs cannot communicate by default. When we learnt about VLANs, we said that each VLAN is usually on its own subnet, switches mainly operate at layer 2 of the OSI model and therefore they do not examine the logical addresses. We will learn how it works, consider the various methods that can be used to implement it, configure inter-VLAN routing using router-on-a-stick and traditional inter-VLAN routing, compare the two styles of implementation and finally verify and troubleshoot inter-VLAN routing.

In this chapter, we will discuss the role played by inter-VLAN routing in communication between different VLANs. In many enterprises, you will find that information sharing across departments is a requirement, therefore, the question begs, how do you make users in the SALES and FINANCE department communicate, yet they are on different VLANS?
a user in FINANCE, would not be able to send a message to a user in SALES since they are on different broadcast domains. The use of VLANs means that users would not be able to communicate across departments, i.e. In previous chapters, we learnt how VLANs segment broadcast traffic on a switch and segment a switched network into different LANs, we also learnt how VLAN information can be transmitted to other switches in the network using VTP and how we can avoid layer two loops using STP.Ĭonsider, this, as the network administrator, one of your tasks is to create and assign different users to VLANs in your network, you have three main departments which should be logically segmented using VLANs, VLAN 10 – FINANCE, VLAN 20 – SALES and VLAN 30 – HR.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
